-STACKS
(im using dashes to maintain the indentation here)
--creating the structure
Struct stack
{
Char data [MAX];
int top;
};
--declaring the functions
char pop (struct stack *stk);
void push (struct stack *stk, char item);
--initializing in Main Program(Function)
main()
{
stack s;
s.top = -1;
push( &s , "A" ) // Calling the Push Function while inserting letter "A" into a stack
pop( &s ) // Removing the element
}
--PUSH Function
void push (stack *stk, char item)
{
If (stk ->top < MAX -1)
{
stk->top++;
stk->data[stk->top] = item;
}
Else
printf(“stack is full \n”);
}
--POP Function
char pop (stack *stk)
{
If(stk->top > -1 )
{
char x = srk -> data[stk->top];
stk->top--;
return x;
}
Else
{
printf(“stack is empty \n”);
return 0;
}
}
Simple C Programing with TrazoR
http://simplec.tk/
Google It, You'll Get It.
Monday, March 28, 2011
Stack - Real Life Example - Plates in Dispenser
EBook to learn stacks _ Free
Stacks - Introduction
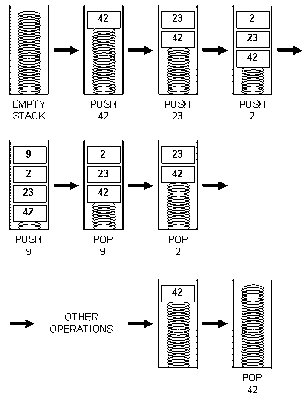
-Stack is the First Data Structure in Programming.
-It is a method where we use LIFO ( LAST IN - FIRST OUT ).
LIFO stacks, also known as "push down" stacks, are the conceptually simplest way of saving information in a temporary storage location for such common computer operations as mathematical expression evaluation and recursive subroutine calling.
-It has only two fundamental operations called PUSH and POP.
--PUSH > to insert an element ( to the top )
The push operation adds an item to the top of the stack,
hiding any items already on the stack, or initializing the stack if it is empty.
--POP > to remove an element ( from the top )
The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack, and returns this value to the caller. A pop either reveals previously concealed items, or results in an empty stack.
-It is a method where we use LIFO ( LAST IN - FIRST OUT ).
LIFO stacks, also known as "push down" stacks, are the conceptually simplest way of saving information in a temporary storage location for such common computer operations as mathematical expression evaluation and recursive subroutine calling.
-It has only two fundamental operations called PUSH and POP.
--PUSH > to insert an element ( to the top )
The push operation adds an item to the top of the stack,
hiding any items already on the stack, or initializing the stack if it is empty.
--POP > to remove an element ( from the top )
The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack, and returns this value to the caller. A pop either reveals previously concealed items, or results in an empty stack.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)